研究課題
「階層粉体の基礎物理特性解明と衝突応答」
基盤研究(A) 18H03679
研究目的

本研究では従来の粉体物理研究で採用されてきた「代表粒子サイズ」の概念を拡張し,複数の粒子サイズや粒子間相互作用が階層構造を形成する粉体の物理特性の研究に取り組む.階層粉体は,スケールの大きく異なる粒子群の混合,微小粒子の凝集によるマクロ粒子の生成,付着力の効果が顕著な粒子により構成される粉体のマクロ力学特性などによって特徴付けられる.このような特徴を持つ階層粉体の基礎物理特性の解明に集中する.粉体の構成粒子サイズや相互作用の階層性がその力学特性に及ぼす影響についての系統的研究を行い,階層粉体の物理特性を明らかにすることを目的とする.粒子サイズ等の階層性が単分散粒子群で構成される付着性のない粉体系の挙動を本質的に変化させる要因であるかどうかを主に実験的手法により明らかにする.系統的実験の他に必要に応じて数値計算などの手法も用い,階層粉体の物理的描像を確立することが最終目標となる.
主要研究成果
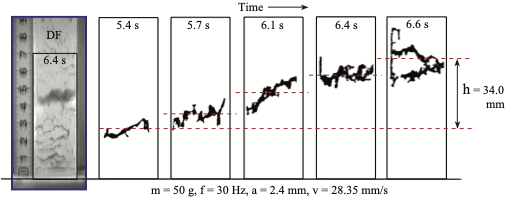
"Impact drag foce exerted on a projectile penetrating into a hierarchical granular bed"
Fumiaki Okubo and Hiroaki Katsuragi
Astron. Astrophys., 664, A147 (2022), DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202243787

研究概要:【衝突】階層的構造を持つ粉体層に固体弾丸を衝突させた際に生じる衝突抵抗力を調べる実験を行っている.硬質な粒子からなる粉体層への衝突と比較すると,階層粉体への衝突では弾丸の浸透深度が比較的大きくなることが分かっている.実験で得られたデータを先行研究のモデルにフィッティングさせたところ,階層粉体における摩擦抗力はモデルのスケーリング関係で予測される値よりもかなり大きいことが分かった.
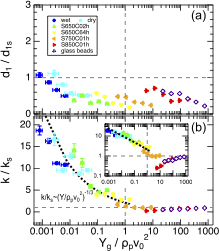
"Decompaction wave propagation in a vibrated fine-powder bed"
Prasad Sonar and Hiroaki Katsuragi
Phys. Rev. E, 106, 014905 (2022), DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.106.014905
研究概要:【振動】微粉末を容器に入れて振動させた場合,単純な圧密のほか,静的な亀裂成長,亀裂の容器情報への移動などのモードがみられることを実験的に見いだした.更に情報に移動する亀裂の移動速度は振動の条件には帆とんど依存せず,重力と微粉末の付着力のバランスにより亀裂の実効的移動が実現されていることを明らかにした.
"Deformation of a rotated granular pile governed by body-force-dependent friction"
Terunori Irie, Ryusei Yamaguchi, Sei-ichiro Watanabe, and Hiroaki Katsuragi
Phys. Rev. E, 104, 064902 (2021), DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.104.064902
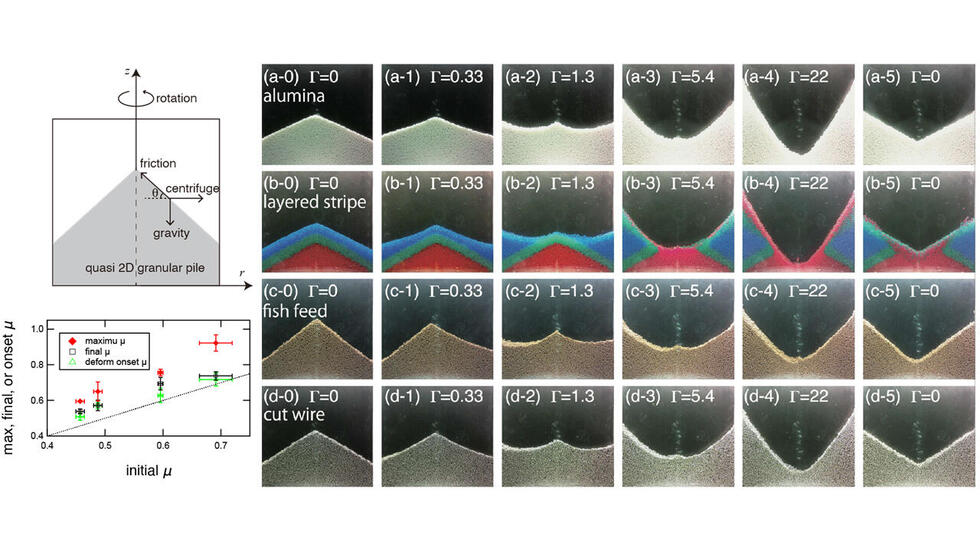
研究概要:【回転によるせん断】砂山(階層構造を持つものと持たないもの両方)に回転遠心力を加え,その変形の様子を観察した.表面変形を摩擦,遠心力,重力の合力により記述するシンプルなモデルの開発に成功し,モデルによる実験結果のフィッティングから粉体摩擦の重力(体積力)依存性を議論することに成功した.また,特に階層粉体構造の付着力の評価についても,Measurement of surface deformation and cohesion of a granular pile under the effect of centrifugal force, T. Irie, R. Yamaguchi, S. Watanabe, and H. Katsuragi, Meas. Sci. Technol., Vol. 32, 125301:1-10 (2021)において評価する手法を確立した.
"Undulating compression and multistage relaxation in a granular column consisting of dust particles or glass beads"
Felipe Pacheco-Vázquez, Tomomi Omura, and Hiroaki Katsuragi
Phys. Rev. Research, 3, 013190 (2021), DOI : 10.1103/PhysRevResearch.3.013190
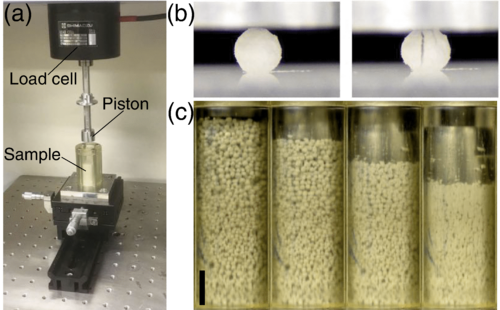
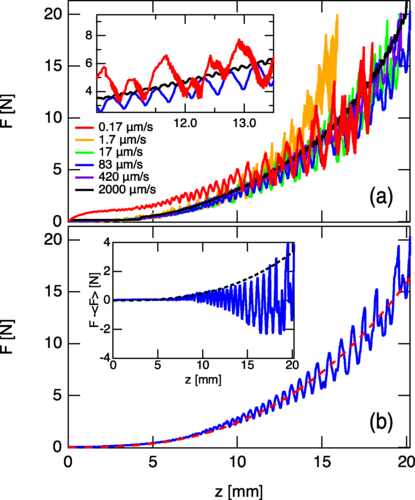
論文概要:【圧縮】粉粒体の階層構造の影響を根本的に特徴づけるため,円筒形セルに閉じ込められたダスト粒子とガラスビーズの一連の圧縮緩和試験を実施した.それぞれの粒子の典型的な直径は約1mmであるが,ダスト粒子は微小な(~ 5µm)ガラスビーズで構成される.実験結果より,双方の粒子において圧縮力はストロークの増加とともに非線形的に増加する.ダスト粒子を用いた際は,圧縮力の増加中に周期的な揺らぎを含む.また圧縮後の時間経過による応力緩和は指数関数と対数関数の組み合わせで表現される.
"Bouncing of a projectile impacting a dense potato-starch suspension layer"
Kazuya Egawa and Hiroaki Katsuragi
Physics of Fluids, 31, 053304 (2019), DOI: 10.1063/1.5095678
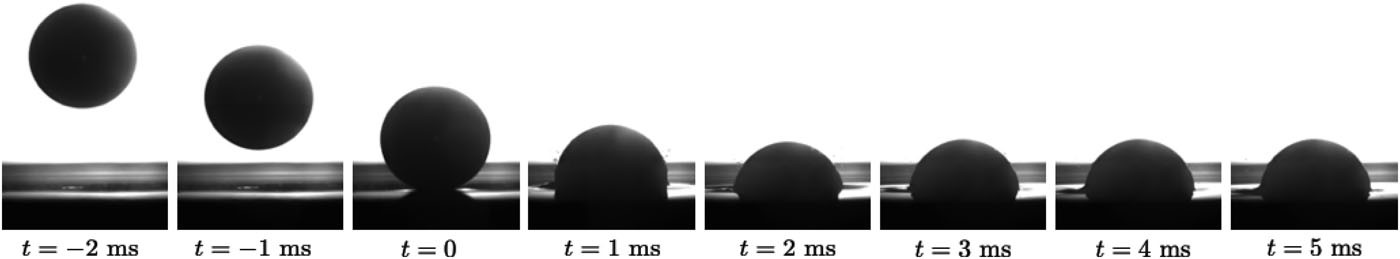
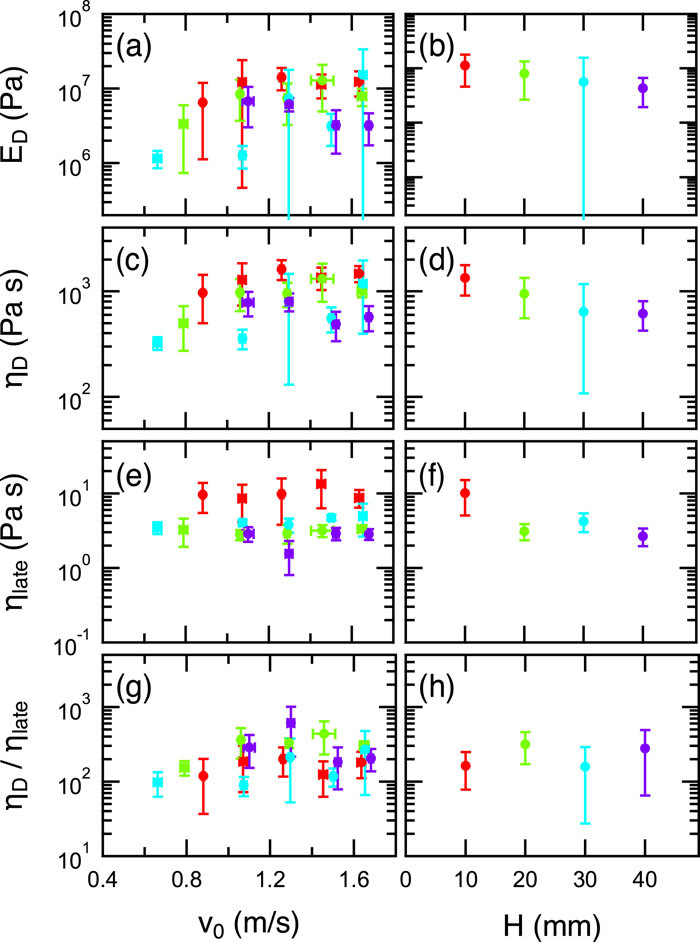
論文概要:【衝突】高密度片栗粉懸濁液(ダイラタント流体)へ固体弾丸を落下衝突させる実験を行った.弾丸の運動データより,反発係数と反発後弾丸が停止するまでの時間を測定した.線形な粘弾性モデルを仮定することで,有効弾性と粘度を推定した.推定された弾性率と粘度は個別に測定された先行研究の結果と一致していた.さらに,衝突後の弾丸の終端速度での沈降を測定することでストークス抵抗を推定した.
"Impact-Induced Energy Transfer and Dissipation in Granular Clusters under Microgravity Conditions"
Hiroaki Katsuragi and Jürgen Blum
Phys. Rev. Lett., 121, 208001 (2018), DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.208001
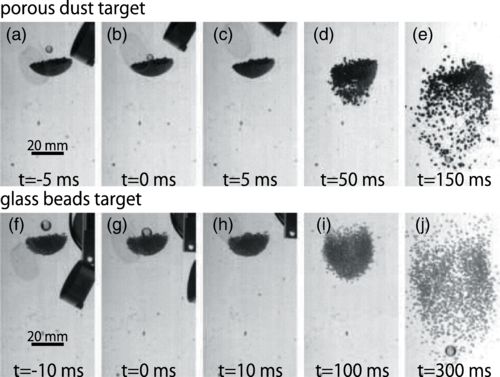
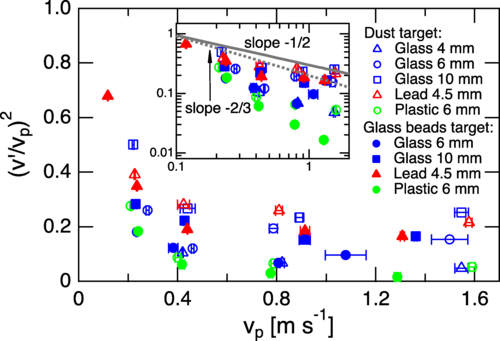
論文概要:【衝突】高さ1.5 mのドロップタワーを使用し,宇宙空間を模擬した微小重力・真空条件下で弾丸の粉体への衝突実験を行った.粉体構成粒子には多孔質のダスト凝集体(軟質)およびガラスビーズ(硬質)を用いた.高速度カメラによる衝突観測の結果,使用する弾丸や粉体に関係なく,衝突により弾丸が保持していた運動エネルギーの約5%が粉体へ伝達されることを発見した.また,衝突エネルギーは衝撃点からターゲットに等方的に伝達されることも明らかになった.
上記以外の本研究プロジェクト関連研究成果
"Vibration-induced fracturing in fine-powders"
P. Sonar and H. Katsuragi
"Grain-size dependence of water retention in a model aggregated soil"
H. Yasuda, M. Katsura, and H. Katsuragi
Adv. Powder Technol.,accepted, (arXiv:2206.01036)
"History-dependent deformation of a rotated granular pile governed by granular friction"
T. Irie, R. Yamaguchi, S. Watanabe, and H. Katsuragi
Adv. Powder Technol., 33, 103629 (2022), DOI: 10.1016/j.apt.2022.103629
"History-dependent growth and reduction of the ripples formed on a swept granular track"
S. Hata, M. Katsura, and H. Katsuragi
Eur. Phys. J. E, 45, 8 (2022), DOI: 10.1140/epje/s10189-022-00165-7
"Measurement of surface deformation and cohesion of a granular pile under the effect of centrifugal force"
T. Irie, R. Yamaguchi, S. Watanabe, and H. Katsuragi
Meas. Sci. Technol., 32, 125301 (2021), DOI: 10.1088/1361-6501/ac1b25
"Force chain structure in a rod-withdrawn granular layer"
F. Okubo and H. Katsuragi
Mod. Phys. Lett. B, 35, 2150206 (2021), DOI: 10.1142/S0217984921502067
"Centroid migration on an impacted granular slope due to the asymmetric ejecta deposition and landsliding"
T. Omura, S. Takizawa, and H. Katsuragi
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 502, 293-299 (2021), DOI: 10.1093/mnras/staa3982
"Grain size effect on the compression and relaxation of a granular column: solid particles vs dust agglomerates"
F. Pacheco Vazquez, T. Omura, and H. Katsuragi
EPJ Web Conf., 249, 07005 (2021), DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/202124907005
"A novel experimental setup for an oblique impact onto an inclined granular layer"
S. Takizawa, R. Yamaguchi, and H. Katsuragi
Rev. Sci. Instrum., 91, 014501 (2020), DOI: 10.1063/1.5127087
"Scaling laws for the oblique impact cratering on an inclined granular surface"
S. Takizawa and H. Katsuragi
Icarus, 335, 113409 (2020), DOI: 10.1016/j.icarus.2019.113409
"Laboratory experiment and discrete-element-method simulation of granular-heap flows under vertical vibration"
D. Tsuji, M. Otsuki, and H. Katsuragi
Phys. Rev. E, 99, 062902 (2019), DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.99.062902
"Physical constraints on sand crab burrows: mechanical properties of wet sand explain the size and spatial distributions of burrows on beaches"
A. Shinoda, S. Fujiwara, H. Niiya, and H. Katsuragi
PLOS ONE, 14, e0215743 (2019), DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215743
"Packing-dependent granular friction exerted on a rod withdrawn from a granular layer: the role of shear jamming"
T. Furuta, S. Kumar, K. Anki Reddy, H. Niiya, and H. Katsuragi
New J. Phys., 21, 023001 (2019), DOI: 10.1088/1367-2630/ab00c8
"Impact-induced collapse of an inclined wet granular layer"
S. Takizawa, H. Niiya, T. Tanabe, H. Nishimori, and H. Katsuragi
Physica D, 386-387, 8 (2019), DOI: 10.1016/j.physd.2018.08.002
"Void structure stability in wet granular matter and its application to crab burrows and cometary pits"
A. Shinoda, S. Fujiwara, H. Niiya, and H. Katsuragi
Sci. Rep., 8, 15784 (2018), DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-33978-8
"Shape dependence of resistance force exerted on an obstacle placed in a gravity-driven granular silo flow"
H. Katsuragi, K. Anki Reddy, and K. Endo
AIChE J., 64, 3849 (2018), DOI: 10.1002/aic.16205